
You’ve probably heard people say, “Bitcoin is anonymous.” That promise of privacy is what makes it so appealing, sending money without banks, names, or anyone watching. But the truth is very different: every Bitcoin transaction is recorded on the blockchain, making it traceable.
But here’s the truth most people don’t realize: every Bitcoin transaction is public, permanent, and traceable.
Bitcoin, the world’s first and largest decentralized digital currency, was invented by an unknown person, but it is widely believed that Satoshi Nakamoto invented Bitcoin. Bitcoin was introduced in 2009 and now has grown to become one of the most reputable and valuable cryptocurrencies in the world, with a market capitalization of $1 trillion.
Every crypto transaction leaves a trace. Whether you're sending coins to a friend or falling for a fake trading platform, it can be tracked with the right tools.
And as crypto crimes surge, governments, cyber experts, and even private firms are getting better at tracing Bitcoin through the blockchain.
In this article, we’ll break down how Bitcoin works, whether transactions can be traced, and what that means for privacy, fraud, and crypto recovery.
Table of Contents
Yes, Bitcoin is traceable, and it is with the blockchain that all its transactions are recorded. A blockchain is a distributed and decentralized database used to record all crypto transactions. Each transaction is stored in a block on the blockchain and becomes permanent once added.
During any exchange of Bitcoins, the data sent always includes the sender's address, the receiver's address, and the number of Bitcoins transferred. These addresses are just combinations of alphanumeric characters unique to every Bitcoin wallet.
However, the address neither identifies who is really sending the Bitcoins nor who is receiving them; it leaves a record of all transactions, which is public. While studying the movement, we can still trace back the address of that Bitcoin even without finding out who actually owns it.
Many people think tracking Bitcoin is difficult, but it’s simpler than you might expect. Bitcoin runs on the blockchain, a public record that shows every transaction. This means anyone can follow where coins move from one user to another.
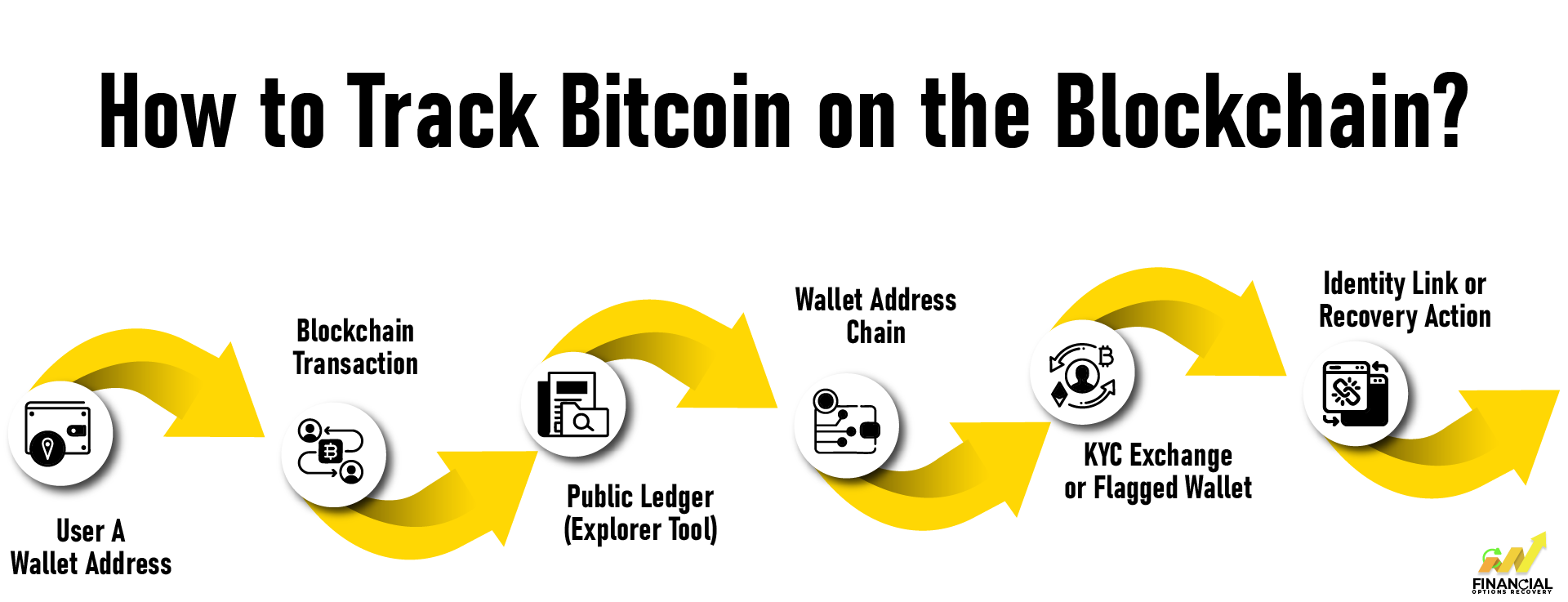
Here’s how tracking works in simple terms:
Every time Bitcoin is sent or received, the transaction details, including wallet addresses, amounts, and timestamps, are permanently recorded on the blockchain. This transparent record is available for anyone to view.
By close observation of the streams of transactions, an analyst can follow the flow and movement of bitcoins over time. Wallet addresses do not directly reveal a person’s identity. However, if the wallet connects to a regulated exchange or service with KYC data, the transactions might be traced to real-world individuals.
The transaction sequence is analyzed to track Bitcoin's chronological path. Wallet addresses usually aren’t linked to a person or business. But if a wallet connects to a regulated exchange that collects KYC details, those transactions can be traced to a real identity.
Blockchain analytics enables the tracking of suspicious patterns and wallet clusters. They also monitor mixer or tumbler addresses using machine learning and data analysis. This helps trace and recover stolen or fraudulent Bitcoin after scammers try to hide their tracks.
Scammers use all kinds of tricks to hide what they’re doing, which makes getting stolen Bitcoin back pretty tough. But thanks to powerful blockchain tools and tracking technology, it’s now possible to trace where the money went even when scammers try to cover their tracks.
|
Scam Method |
How It Works |
Traceability Challenge |
How Blockchain Analytics Helps Detect |
|
Mixing/Tumbling Services |
Scammers send stolen Bitcoin through services that mix coins from many users to obscure the origin. |
Mixing obfuscates transaction paths by pooling and redistributing coins. |
Advanced tools analyze transaction timing, amounts, and wallet clustering to unravel mixing patterns and trace funds. |
|
Fraudsters create fake or unregulated exchanges to steal deposits or personal data. |
Initially, it bypasses KYC and regulatory checks, making identity harder to trace. |
Blockchain analysis tracks the flow of funds from fake exchange wallets, revealing suspicious movement and connections. |
|
|
Phishing Wallets |
Scammers trick victims into revealing private keys or seed phrases via fake sites or emails. |
Once scammers control wallets, transactions appear normal but are unauthorized. |
Analytics detect unusual wallet activity, like sudden transfers or funds moving to known scam addresses. |
|
Ponzi Schemes |
Operators pool investor funds and redistribute money fraudulently to early investors to appear legitimate. |
Funds are mixed within the scheme’s wallets, making individual tracing complex. |
Forensic tools trace outgoing transactions and wallet connections to expose fraudulent networks. |
|
Ransomware Payments |
Criminals demand Bitcoin payment after locking user data or systems. |
Payments are often routed through multiple wallets or mixers to hide the trail. |
Tracking ransom payments through known ransomware wallet addresses and transaction patterns helps identify perpetrators. |
|
Fake ICOs/Token Sales |
Scammers offer fraudulent token sales to collect Bitcoin or other crypto. |
Funds move quickly through many wallets to avoid detection. |
Monitoring wallet activity and token distribution patterns assists in identifying scam wallets and victim funds. |
Bitcoin isn’t as anonymous as many people think. Every payment is recorded on the blockchain, leaving a permanent trail. This makes it possible to trace stolen Bitcoin, especially if scammers use exchanges or services that require identity checks.
If you’ve been scammed, acting quickly matters. Experts can follow these blockchain trails and improve the chances of recovering your funds. Stay alert, use secure platforms, and never share sensitive information online.
If you believe you’ve been a victim of a scam or need help tracing your Bitcoin, don’t hesitate to contact Financial Options Recovery for expert support.
No, Bitcoin is not completely anonymous. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger (the blockchain), which allows anyone to trace wallet addresses and transaction histories. While personal names aren't attached, addresses can often be linked to real identities through exchanges or metadata.
To avoid traceable errors:
Use trusted wallets, avoid shady sources, skip illegal mixers, and double-check addresses with blockchain tools before accepting funds. Stick to clean, regulated platforms.
The following are some warning signs to identify a fraudulent bitcoin trading platform:
Yes. If scammers use regulated exchanges with KYC or make mistakes when mixing coins, blockchain tools track their funds and help identify them.